Transformation from FinTech 1.0 to FinTech 3.0

China is the Asian leader of Fintech in terms of investment volume and proliferation. China has most number of Fintech Unicorns in Asia and claims more than 35% global Fintech Unicorns. According to Brookings 2018, (out of 27 Fintech Unicorns, 9 are from China). Singapore is the FinTech hub for Southeast Asia. Singapore has an integrated, all encompassed FinTech strategy and a mature, streamlined and stringent regulatory framework. Asia is emerging as the epicentre for Fintech, driven by the need for financial inclusion and resulting mass adoption. The Figure 1.1, classify the Fintech industry under four distinct categories in three transformational waves, Fintech 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0. Internet Plus Asia’s classification of Fintech industry under three waves could be different to text book definition of Fintech 1.0, Fintech 2.0, Fintech 3.0 which are mostly in line with the evolution of banking industry in 20th and 21st century. But Internet Plus Asia’s focus is limited to post 2010 developments of Fintech ecosystems and it will showcase progressive Fintech start-ups and Unicorns in Asia under these 4 categories.
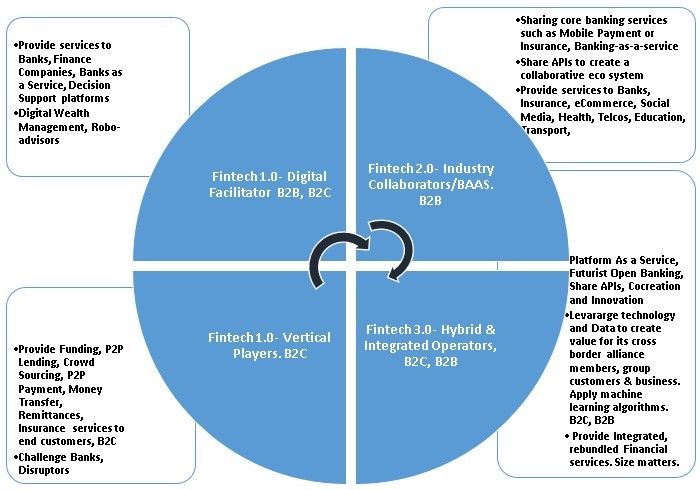
Figure 1.1 – Internet plus Asia’s scope and classification of Fintech in 4 dimensions under three waves. Transitioning Fintech from Fintech 1.0 to Fintech 3.0
2.0 FINTECH 1.0 – VERTICAL PLAYERS AND DIGITAL FACILITATORS
Unbundling of Banking is reflected in the 1st wave of Fintech (Fintech 1.0) and it is demanded by the Millennial as more transparency and user freedom in banking and insurance transactions are needed by them. Therefore more and more standalone Fintech 1.0 apps had sprouted up in Payment, Lending, P2P, Wealth Management and Insurance spaces.Though Fintech 1.0 players disrupt the incumbent operators in some way, they generate revenue for banks indirectly or directly in a complementary fashion. Most of these apps in some way are dependent on traditional banking infrastructure. This is co-optition or co-operative competition or "marriage of convenience".
2.1 FINTECH 1.0 - VERTICAL PLAYERS, B2C
This group is more focussed on serving under-banked and un-banked, SMEs, students that have high risk profiles for lending. High net-worth customers mostly stick with existing incumbent banks. Frictionless mobile payments, money transfer, micro insurance for niche markets, short term funding for SMEs, lending for needy segments like students dominate the start-ups in the 1st wave.

Figure 2.1: Examples for P2P money transfer & mobile payments apps in Asia, Fintech 1.0

Figure 2.2: Online Lending, P2P Crowd Funding apps in Asia – Fintech 1.0
2.2 FINTECH 1.0 – DIGITAL FACILITATORS B2B
Digital Facilitators primarily cover Digital Wealth Management, automated financial advisory solution such as asset management and Robo-advisors on B2C and B2B platforms.
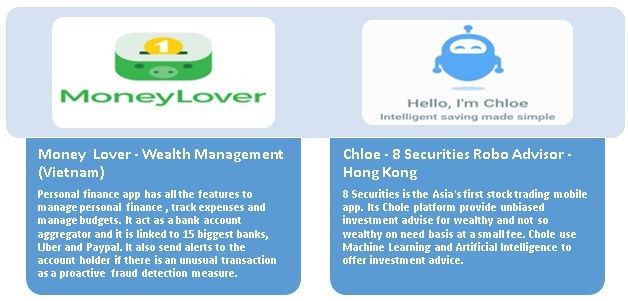
Figure 2.3: Wealth Management apps in Asia – Fintech 1.0
3.0 FINTECH 2.0 – INDUSTRY COLLABORATORS / BANKING-AS-A-SERVICE, B2B
Incumbent Banks and Insurance giants are in a uniquely privilege position to exploit the "internet Plus Finance" revolution by opening their APIs such as account creation, create /update customer, create / update loans etc. (via a company middleware or a common industry middleware), enabling 3rd party Fintech start-ups and businesses to co-create value added products in a "plug and play", modular fashion, leveraging treasure trove of customer data. Currently they partner with 3rd parties mostly for improving customer experience, without cannibalizing their core services much. Banks APIs are mainly used by following parties
1. External 3rd party developers who build apps for market extension,
2. Business partners for partner integration
3. Internal developers to enhance customer experience
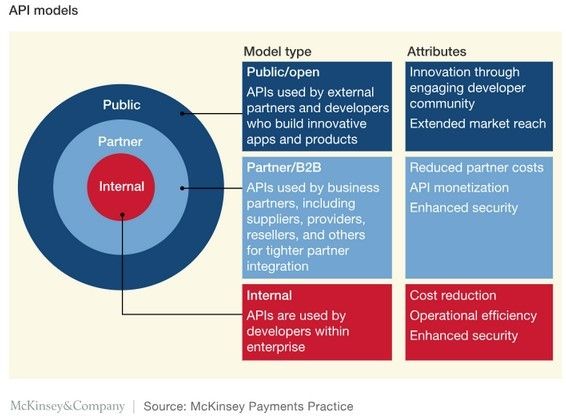
Figure 3.1: API sharing internally and externally
DBS bank’s strategies of going all digital from banking to CRM (customer relationship management) and open banking have following advantages
1. Single Login for all the apps. Earlier different apps were used for different services.
2. AI driven digital assistance help customers to reach Digibank and surf virtually with minimum effort, driven contextually (example: Chatbot)
3. Open APIs help to connect external developers and business partners. World’s biggest API developer platform of DBS have access to breadth of services such as funds transfer and peer-to-peer payment service PayLah. By exposing DBI’s APIs, DBI can increase the product portfolio automatically through 3rd party Fintechs. It also empower bank’s corporate clients to manage their accounts in an optimum and timely manner without much intervention by the bank. DBI even conduct hackatons to get Fintechs involved in new product releases.
Pasar Polis, a Fintech in Indonesia, is also a good example for collaboration and Banking as a Service with different industries creatively. (See Fig 3.2) Pasar Polis creates an additional channel for incumbent Insurance companies by placing their products via APIs, to extend their marketplace wider. Pasar Polis had become an Insurance company in a mutually beneficial way thanks to open APIs while customers are getting a wider choice.

Figure 3.2: Examples for Banking as a Service. DBS help industries to set up banking functions and Pasar Polis help industries to set up insurance – Fintech 2.0
4.0 FINTECH 3.0 – HYBRID AND INTEGRATED OPERATORS, PLATFORM AS A SERVICE B2C AND B2B
The three entities illustrated in Figure 4.3 are classic examples for Fintech 3.0 or next generation fintech.It is extremely difficult to predict the future. But following trends can revolutionize the Asian and Global Finance and Fintech industry. The scale of operations and openness in Fintech 3.0 companies will make small Fintech companies to become satellite operators of the giants such as BAT (Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent), JD.com and Pingan. Fintech 3.0 will bring together many players across different marketplaces, gravitating towards big players like BAT, forming different planetary eco systems governed by openness, integration and technologies such as API sharing, cloud, AI, machine learning, blockchain and big data.
1. Platform Driven
Ant Financial and We Chat Finance are two examples for a Platform Driven Finance Service in Fintech 3.0 era. In Fintech 3.0, customers can access so many disparate finance apps with single login on a unified single platform like Ant Financial (Figure 4.1) or We Chat (Figure 4.2).
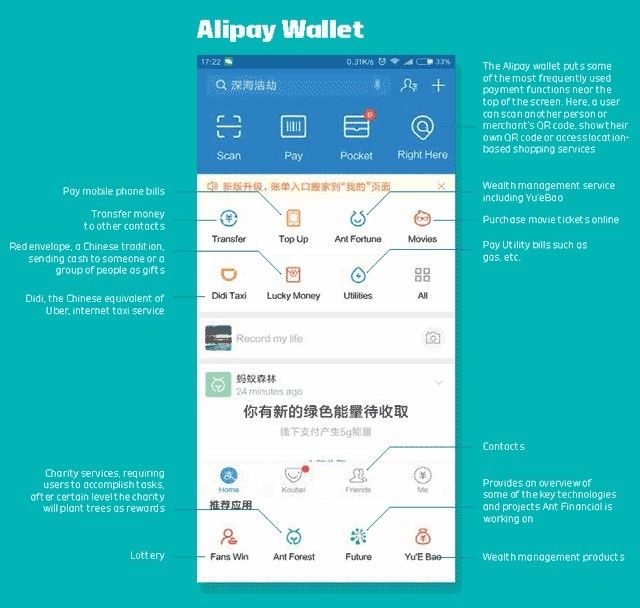
Figure 4.1: Alipay Wallet Source: chinainternetwatch.com
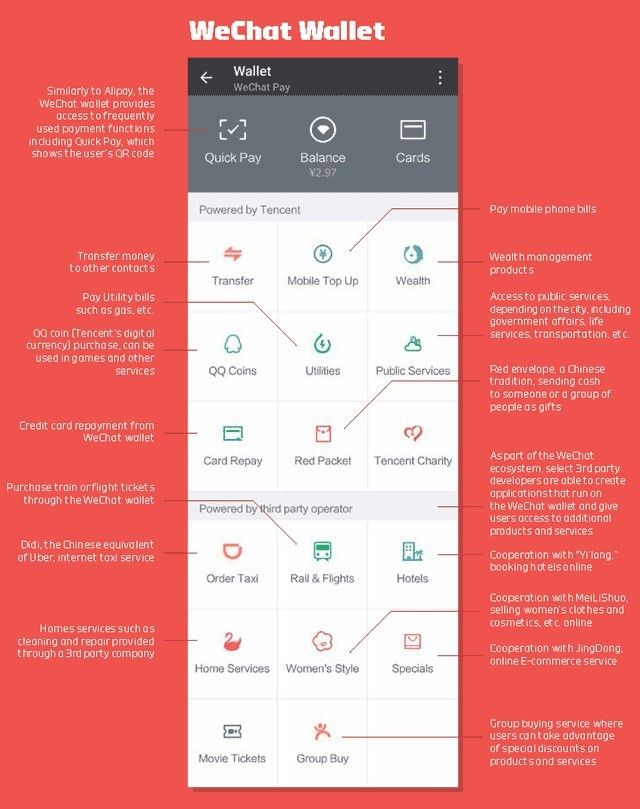
Figure 4.2: WeChat Wallet Source: chinainternetwatch.com
Both Ant and WeChat’s galaxy of product portfolio, convergent in a single app seamlessly and contextually. These can be called as “Super Apps” where e Commerce, search, communication, payments and other finance apps are bundled into one platform. Customers lovingly embrace these “one-stop-shop” apps due to convenience.
2. Cross Service Integration, Un-bundling to Re-bundling
Customers prefer to deal with one Fintech company for all the services rather than accessing different services from different Fintechs. Unbundling of financial services in Fintech 1.0 (the generation represent the diversity) had been transformed to re-bundling in Fintech 3.0 due to the user preference for convergence or aggregation in a contextual and seamless manner.
3. Open Marketplace
Future generation apps like Ant Financial release APIs, to enable 3rd party developers to have access to capabilities of the ant financial platform and its treasure trove, data. Ant Financial had extended "open marketplace" concept adopted by Taobao and TMall, C2C/B2C online bazar for e-tailing, by introducing Caifu Hao where 3rd party Fintech developers host their 3rd party apps on Ant Finance platform. Taobao provided online storefronts for millions of merchants while Ant can now provide store fronts for Fintech. Through this customers gain more choice for finance goods such as insurance and fixed term deposit products. Banks, insurance companies and securities can host their store fronts in Caifu Hao. This next generation platform have access to analytics related customer profile giving more autonomy and control for merchants, similar to T Mall and Taobao online trading platforms of Alibaba. Ant Financials run its insurance portal to compare prices and sell large number of insurance policies of more than 80 insurance companies.
4. Industry and Cross Border collaboration, not disrupting the finance industry
China Construction bank, Pudong Development Bank, Huaxia Bank, China Everbright Bank had paired up with Ant Financial to develop futuristic applications using blockchain, AI, cloud and biometric technologies. Ant Financial had also partnered with Standard Chartered Bank to leverage Bank's expertise across the "Belt and Road" countries and Ant's technological superiority of its platform. The primary strategy adopted by Ant to reach global markets is to partner with leading local payment players such as Pay Tm (India), Kakao Pay (South Korea), Ascend (Thailand), TouchnGo (Malaysia), napass (Vietnam), PiPay (Cambodia), Emtek (Indonesia).
5. Powered by Big Data, AI, Machine Learning and Cloud Computing
Banks cannot decide the credit worthiness of SMEs. But Ant Financials can underwrite credit of small merchants in Taobao platform through Sesame Credit by leveraging big data in Taobao e commerce platform, shared Machine Learning and AI platforms of Alibaba. It can also detect fraud. Therefore SME is a new financial market created by Fintech 3.0 such as Ant Financial.
6. Finance Clouds, API sharing will dominate the scene

Figure 4.3: Examples for Platform as a Service – Fintech 3.0
Share This
Details
Mothilal is a Co Founder of Internet Plus Asia, a co-creation platform for tech start-ups in Asia. Prior to this he was a Chief Executive Officer, Chief Strategy Officer, Chief Corporate Officer and Chief Operating Officer of number of Telecommunications and IT companies in Asia and Pacific regions for over 20 years. He is a turnaround specialist and a strategist. As CEO and C level executives, he was responsiblefor transformation and turning around many telecos. He was also instrumental in winning many international awards for these companies such as GSM awards in 3 consecutive years, International Asia Pacific Quality Award, Asia CSR award. He has obtained the Doctor of Business Administration from PPA Business School, Paris, receiving a Distinction for his DBA research, "Corporate Venture Capital as an engagement model to Co-create 5G ready services in Telco - Startup collaboration"











